Hello, everyone. In this article, I will discuss a handy feature of Linux: “Crontab.” It is used to schedule tasks and is one of the most useful features for server administrators.
Some tasks, like backups and updates, need to be repeated repeatedly. This becomes harder when you have more than one server to manage.
To solve this problem, crontab a time/date/month/hour that you specify.
So, let us learn how to use crontab and schedule your tasks.
Opening Crontab
To open crontab, then open your terminal and type
crontab -e
If you are using it for the first time, then it will show you something like this -

You can use any text editor you want. I prefer Vim (the second option), but if you are a newbie to Linux, you can use the Nano editor (the first option).
If your task requires admin privileges to execute the command, you must open crontab using this command
sudo crontab -e
Note — crontab -e and sudo crontab -e both are representing a different file.
Basic Usage
Crontab has a particular syntax to declare any task to be scheduled.
Syntax
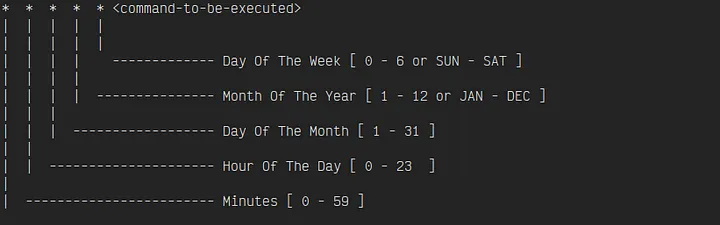
* * * * * <command-to-be-executed> <arguments>
So, in the above syntax, every position in which * is present represents something.
Here are the details of what each position means in the above syntax.
In the syntax, some symbols are also used. These are:
*- Represents Every,-Value List Separator-- Range Of Values/- Step Values
Examples
So let us have some examples -
Command to run a script every minute
* * * * * db_backup.sh
The above command will run the backup script every minute.
Command to run a script at 00:00 every day
0 0 * * * db_backup.sh
Command to run a script at 5 am every day
0 5* * * db_backup.sh
Command to run the script every Sunday at 5 am
0 5 * * SUN db_backup.sh
The above command can also be written as
0 5 * * 0 db_backup.sh
Command to run a script on weekdays
* * * * 1-5 db_backup.sh
The above command can also be written as
* * * * MON-FRI db_backup.sh
Command to run the script on starting of every month
0 0 1 * * db_backup.sh
Command to run the script at the beginning of the last month of every year
0 0 1 12 * db_backup.sh
Command to run the script at 10:50 am every day
50 10 * * * db_backup.sh
Command to run the script every 30 minutes
*/30 * * * * db_backup.sh
So these are some examples I have taken to help you understand how to schedule a task using crontab.
Shortcuts
So there above we have learned to write a task in crontab.
- @reboot — Run once at startup
- @yearly — Run once a year
- @annually — Run once a year ( Same as @yearly )
- @monthly — Run once a month
- @weekly — Run once a week
- @daily — Run once a day
- @midnight — Run once a day at midnight ( Same as @daily )
- @hourly — Run once an hour
Example
@reboot db_backup.sh
Some other commands
- To list all cron jobs
crontab -l
- To remove all cron jobs
crontab -r
- To enter crontab for a particular user
crontab -u <username> -e
This is all about crontab. I hope you have found this article useful. If you have any problems, ask me in the command section.